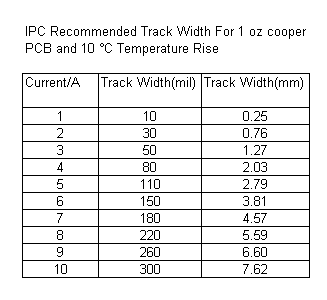
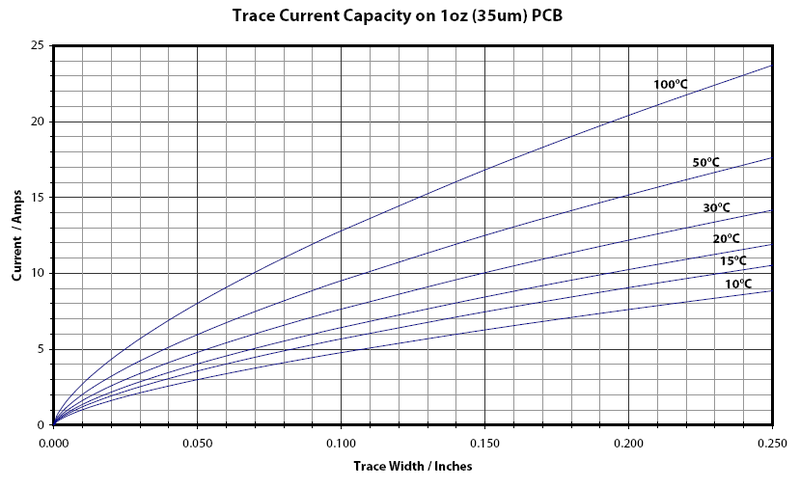
Table of Contents:
- Importance of a PCB Trace Width Calculator
- Why Use a Trace Width Calculator?
- What is a PCB Trace Width Calculator?
- FAQs About Calculating Trace Width
Importance of a PCB Trace Width Calculator
No matter what industry you work in, you likely use printed circuit boards (PCBs) daily. These devices are vital to the function of electronics and connect and mechanically support electrical components to ensure proper operation.
Whether you use PCBs to sustain medical equipment, lighting technology or consumer electronics, they should operate using the proper trace width. With our trace size calculator, you can ensure your printed circuit boards are safe and functional at all times.
Why Use a Trace Width Calculator?
Trace calculators allow users to accurately determine the width of a printed circuit board conductor, or “trace,” using programmed formulas. Trace width is a vital parameter in PCB design and layout. It is necessary for carrying currents through printed circuit boards while keeping trace temperature increases below a specific input value to prevent overheating.
Trace thickness calculators determine the maximum allowable current that can flow through a PCB without damaging it.
What is a PCB Trace Width Calculator?
You can use our calculator to determine various trace components, such as trace temperature, maximum current, resistance, voltage drop and power dissipation. You can better understand your calculator results by becoming familiar with the following formulas.
Max Current
You can calculate maximum current by using the formula A = (T x W x 1.378 [mils/oz/ft2]).
The values in this formula correspond with the following parameters:
- A: Cross-section area.
- [mils2] T: Trace thickness.
- [oz/ft2] W: Trace width.
Once you’ve worked through the previous equation, you’ll determine the maximum current using IMAX = (k x TRISEb) x Ac.
The fields for this formula are as follows:
- [mils] IMAX: Maximum current.
- [A] TRISE: Maximum desired temperature rise.
- [°C] k, b and c: Constants.
Trace Temperature
Trace temperature is another important element in calculating trace width. The formula for determining trace temperature is TTEMP = TRISE + TAMB.
Assessing trace temperature requires nothing more than three total parameters. The values read as follows and are calculated in Celsius:
- TTEMP: Trace temperature.
- TRISE: Maximum desired temperature rise.
- TAMB: Ambient temperature.
Resistance Calculation
When calculating trace resistance in your PCB, you’ll begin by converting the cross-section area from [mils2] to [cm2] following the formula A’ = A * 2.54 * 2.54 * 10-6.
After working through the equation, you’ll quantify the trace resistance using R = (ρ * L / A’) * (1 + α * (TTEMP – 25 °C)).
The values in these formulas correspond with the following quantities:
- T: Trace thickness.
- [oz/ft2] W: Trace width.
- [mils] R: Trace resistance.
- [Ω] ρ: Resistivity parameter.
- [Ω · cm] L: Trace length.
- [cm] α: Resistivity temperature coefficient.
- [1/°C] TTEMP: Trace temperature.
Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage drop is the decrease of electrical potential as it moves through a current in an electrical circuit. The equation for determining voltage drop is VDROP = I * R.
The three values in this formula are:
- VDROP: Voltage drop.
- [V] I: Maximum current.
- [A] R: Trace resistance.
Power Dissipation Calculation
Power dissipation occurs when an electrical device generates heat, resulting in energy loss or waste. It is calculated using the formula PLOSS = R * I2.
Each of these quantities reads as follows:
- PLOSS: Power loss.
- [W] R: Resistance.
- [Ω] I: Maximum current.
FAQs About Calculating Trace Width
Calculating trace can be a confusing process for those who are new to using trace thickness calculators. If you have questions regarding our calculator, the formulas or your results, you might find an answer in the following FAQs:
- What unit of measurement is mils? “Mil” gets its name from the Latin term, “mille,” meaning “thousand.” A mil is one one-thousandth of an inch.
- What is temperature rise in this context? Temperature rise is the difference between your PCB’s maximum safe operating temperature and its usual operating temperature.
- Does this calculator have a limit to the amount of current for which it can calculate width? Yes. Based on the formulas, the tool can only calculate trace width of up to 400 mils, 35 amps, copper of 0.5 to 3 ounces per square foot and a temperature rise between 10 and 100 degrees Celsius. The calculator will extrapolate the data when used outside these ranges.
- Why does the calculator show that internal trace widths should be higher than external traces? External trace layers have a high heat transfer, while internal layers do not conduct heat as well, meaning internal traces can store more heat.
Use Our Trace Calculator for Your PCBs Today
If you’re looking to protect your PCBs from damage and overheating, our trace size calculator will help you determine the appropriate widths. You can purchase high-quality PCBs from a circuit board technology leader when you buy from Millennium Circuits Limited.
Contact us for more information on our products today!